Face of the giant panda sign
Medical condition
| Face of the giant panda sign | |
|---|---|
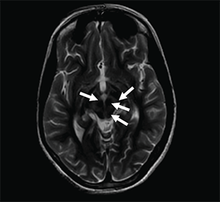 | |
| Axial T2-weighted MRI of the brain at the level of the midbrain showing the characteristic ‘face of the giant panda’ sign, with normal red nuclei and substantia nigra (pars reticulata) against a background of hyperintensity in the tegmentum, as well as hypointensity of the superior colliculi | |
| Complications | choreoathetosis |
| Differential diagnosis | Wilson's disease, Wernicke's encephalopathy, Leigh syndrome, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, toxic leukoencephalopathy, rabies |
| Medication | penicillamine, thiamine, corticosteroids |
The face of the giant panda sign, panda sign of the midbrain or double-panda sign is a characteristic "panda's face" appearance in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of people with Wilson's disease. Along with Kayser–Fleischer rings, the sign is helpful in diagnosis.[1]
While the sign is most common in Wilson's disease, it has been rarely reported in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis,[2] rabies encephalopathy,[3] toxic leukoencephalopathy[4] and Leigh syndrome.[5]
References
- ^ Kuruvilla, A.; Joseph, S. (2000). "'Face of the giant panda' sign in Wilson's disease: Revisited". Neurology India. 48 (4): 395–6. PMID 11146611.
- ^ Nagabushana, D.; Kumar, SP.; Nagaraj, K. (2020). "Giant Panda in ADEM". Neurol India. 68 (3): 720–1. doi:10.4103/0028-3886.289008. PMID 32643704. S2CID 220437811.
- ^ Jassi, P.; Attri, A.; Dhawan, R.; Kakkar, C.; Saggar, K. (2016). "MR imaging in rabies encephalopathy: A rare entity". Ann Indian Acad Journal. 19 (1): 125–8. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.167712. PMC 4782530. PMID 27011645.
- ^ Bimbato, EM.; Carvalho, AG.; Reis, F. (2015). "Toxic and metabolic encephalopathies: iconographic essay". Radiol Bras. 48 (2): 121–5. doi:10.1590/0100-3984.2013.1923. PMC 4433303. PMID 25987753.
- ^ Sonam, K.; Bindu, P.; Gayathri, N.; Khan, N.; Govindaraju, C.; Arvinda, H.; Nagappa, M.; Sinha, S.; Thangaraj, K.; Taly, A. (2014). "The "double panda" sign in Leigh disease". J Child Neurol. 29 (7): 980–2. doi:10.1177/0883073813484968. PMID 23599247. S2CID 5969381.
Further reading
- Das, Shyamal K.; Ray, Kunal (2006). "Wilson's disease: An update". Nature Clinical Practice Neurology. 2 (9): 482–493. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0291. PMID 16932613. S2CID 205340375.
- Jacobs, D. A.; Markowitz, C. E.; Liebeskind, D. S.; Galetta, S. L. (2003). "The "double panda sign" in Wilson's disease". Neurology. 61 (7): 969. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000085871.98174.4E. PMID 14557570.
- Shivakumar, R.; Thomas, S. V. (2009). "Teaching Neuro Images: Face of the giant panda and her cub: MRI correlates of Wilson disease". Neurology. 72 (11): e50. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000344409.73717.a1. PMID 19289731.
- Liebeskind, D. S. (2003). "Faces of the giant panda and her cub: MRI correlates of Wilson's disease". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 74 (5): 682. doi:10.1136/jnnp.74.5.682. PMC 1738451. PMID 12700322.
- Gupta, A.; Chakravarthi, S.; Goyal, M. K. (2014). "'Face of giant panda': A rare imaging sign in Wilson's disease". QJM. 107 (7): 579. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hct217. PMID 24170891.
- Parekh, J. R.; Agrawal, P. R. (2014). "Wilson's disease: 'face of giant panda' and 'trident' signs together". Oxford Medical Case Reports. 2014 (1): 16–17. doi:10.1093/omcr/omu005. PMC 4369968. PMID 25988011.
- Singh, P.; Ahluwalia, A.; Saggar, K.; Grewal, C. S. (2011). "Wilson's disease: MRI features". Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences. 6 (1): 27–8. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.84402. PMC 3173909. PMID 21977083.
- Sonam, Kothari; Bindu, P.S.; Gayathri, Narayanappa; Khan, Nahid Akhtar; Govindaraju, C.; Arvinda, Hanumanthapura R.; Nagappa, Madhu; Sinha, Sanjib; Thangaraj, K.; Taly, Arun B. (2014). "The "Double Panda" Sign in Leigh Disease". Journal of Child Neurology. 29 (7): 980–982. doi:10.1177/0883073813484968. PMID 23599247. S2CID 5969381.
External links
- Radiopedia.org
- v
- t
- e












